Need help? We're here to assist you!
Thank You for Enquiry, we will contact you soon!
Close
The Class 9 is an important year in a student’s life and Maharashtra State Board Social Science Geography is one of the subjects that require dedication, hard work, and practice. It’s a subject where you can score well if you are well-versed with the concepts, remember the important formulas and solving methods, and have done an ample amount of practice. Worry not! Home Revise is here to make your Class 9 journey even easier. It’s essential for students to have the right study material and notes to prepare for their board examinations, and through Home Revise, you can cover all the fundamental topics in the subject and the complete Maharashtra State Board Class 9 Social Science Geography Book syllabus.

Q 1. Answer in brief.
(a) What is mechanical weathering?
(b) What are the main types of chemical weathering?
(c) How does biological weathering occur?
(d) Distinguish between weathering and mass wasting.
Answer a: Mechanical weathering is the process of breaking big rocks into little ones. This process usually happens near the surface of the planet. Temperature also affects the land. The cool nights and hot days always cause things to expand and contract. That movement can cause rocks to crack and break apart. Mechanical weathering mainly occurs because of the following reasons: Temperature, Frost, Crystal growth, Release of pressure, Water.
Answer b: Chemical weathering is what happens when rocks are broken down and chemically altered. The main types of chemical weathering are Oxidation, Carbonation, Hydration and Solution.
Answer c: Biological weathering is a form of both physical and chemical weathering wherein living organisms directly and indirectly cause the decomposition of rock and other materials. Common inducers of biological weathering include animals, plants, and strange organisms called lichens.
Answer d: Difference between weathering and mass wasting are as follows:
Breaking or weakening of rocks is called weathering. The process of moving down of weathered particles due to gravity alone is called mass wasting.
Mechanical weathering, chemical weathering and biological weathering are the three types of weathering. Rapid mass wasting and slower mass wasting are the types of mass wasting.
Q 2. Write whether the statements are true or false. Correct the incorrect ones.
(a) Climate affects earthquakes.
(b) Mechanical weathering is less effective in humid climates.
(c) Mechanical weathering happens on a large scale in dry climates.
(d) The breaking down of rocks into smaller particles is called weathering.
(e) Lateritic rocks are formed through exfoliation.
Answer a: The statement is false. Tectonic activities affect earthquakes.
Answer b: The statement is true. Mechanical weathering is less effective in humid climate and in arid climates, mechanical weathering is dominant.
Answer c: The statement is true. Mechanical weathering happens on a large scale in dry climates.
Answer d: The statement is true. The breaking down of rocks into smaller particles is called weathering.
Answer e: The statement is false. Lateritic rocks are formed through chemical weathering.
Q 3. Complete the flowchart below.
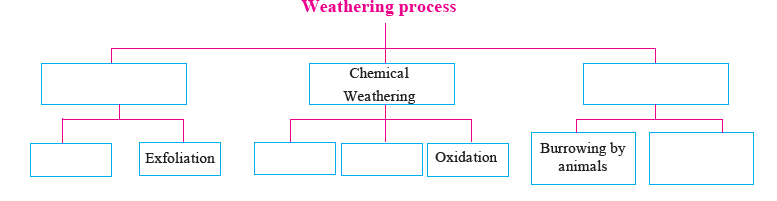
Answer:
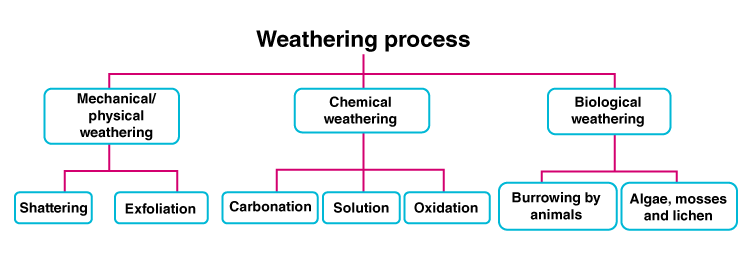
Q 4. Identify the types of weathering from the given description.
(a) Some animals live inside the grounds by making burrows.
(b) The rock rusts.
(c) Water which has accumulated in the crevices of the rocks freezes. Consequently, the rock breaks.
(d) The pipes supplying water in colder regions break.
(e) Sand formation occurs in the deserts.
Answer a: It is called Biological weathering. Biological weathering is a form of both physical and chemical weathering wherein living organisms directly and indirectly cause the decomposition of rock and other materials. Common inducers of biological weathering include animals, plants, and strange organisms called lichens.
Answer b: The rock rusts due to oxidation. An oxidation process occurs in rocks, which have iron present in them. The iron in the rock comes in contact with water and chemical reaction takes place between iron and oxygen. Hence, a reddish coloured layer forms on the rocks. This is called rust.
Answer c: Water, which has accumulated in the crevices of the rocks freezes. Consequently, the rock breaks. It happens due to the action of frost. We know that the volume of the water increases when it freezes. In areas where the temperatures drop below 0o C for quite some time, the water accumulated in the cracks and crevices in the rocks freezes. Its volume increases. This leads to tension in the rocks and they shatter.
Answer d: The pipes supplying water in the colder regions break because of action of frost. In winter the pipes for water supply break or even rocks crack because at temperatures below freezing the water expands. When the water resource expands on freezing it bursts. The water escapes and this can cause serious damage and adverse reactions. This is commonly seen during extreme winters, especially in freezing temperatures.
Answer e: Due to action of temperature sand formation occurs in the deserts. Deserts are formed by weathering processes as large variations in temperature between day and night put strains on the rocks, which consequently break in pieces.